Research on temperature stress correlation of large-span structural space frame
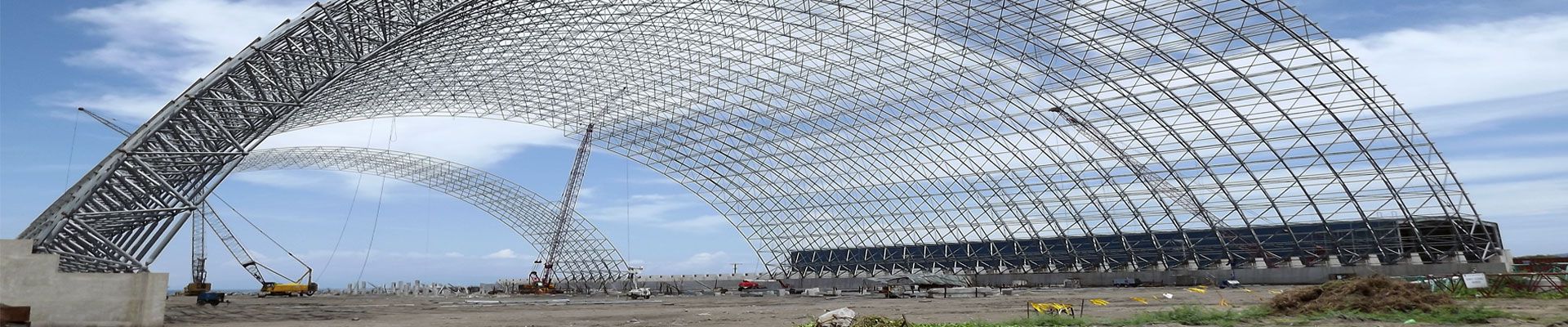
Since modern times, my country’s architectural space structure has developed rapidly, and in the late 1950s, more suspension structures were used. In the late 1990s, lightweight and efficient modern space structures such as string beam structures and string-supported domes were widely used. my country’s spatial structure is developing rapidly, and the scope of application is expanding. The development level of the spatial structure represents the strength of the national construction field. In recent years, my country has attached great importance to the development of large-span spatial structures, and the number of applications of long-span spatial structures has gradually increased, which is widely used in large public places such as stadiums and theaters.
Application and development of building steel structure
The steel structure is the main application material of space structure. There will be a lot of temperature problems in the design of steel structures. In recent years, the weather has become increasingly severe. During the construction of large-span steel structures, uncertain environmental factors have been experienced in the construction of large-span steel structures, from weak structures to strong structures. Under residual stress, the safety of long-span steel structures under extreme weather is worth studying. A large number of temperature effect problems will be encountered during structural design, such as industrial building workshops have an impact on the stress distribution of structural roofs, and the size of structural temperature expansion joints is based on temperature stress. In response to adverse changes in temperature stress, people take countermeasures to reduce the impact on the concrete structure, such as the use of thermal insulation materials to heat the structure. The development of long-span steel structures is relatively mature, and the accumulated deformation of long-span concrete structural members is large. Long-span steel structures are sensitive to temperature changes, and can only rely on the cooperative deformation of structural members to resist temperature deformation. The basic temperature is the main meteorological parameter required to determine the effect of temperature. In the past, building structure design was mostly based on experience. my country’s building structure load code stipulates the basic temperature. The temperature of the concrete structure with slow heat transfer rate is close to the monthly average temperature, and the temperature of the structure with fast heat transfer rate is close to the highest annual temperature. temperature.
Among the existing long-span steel truss arch bridges, the bridge types are divided into Luoze arch and tie-rod arch according to the proportional relationship between the arch rib and the tie beam stiffness. The superstructure of steel truss arch bridge is mainly composed of connection system and deck system. Steel truss bridges have great advantages in road-rail bridges, because of their unique characteristics, it is easy to coordinate with the surrounding landscape; the construction of the upper structure of the bridge is mostly high-altitude operation, and the truss arch bridge members do not need large lifting equipment, and the truss bridge rods Most of the components are axial force bearing components, and the mechanical characteristics of the arch bridge determine that it has better vertical stiffness. The shortcomings of steel truss arch bridges are reflected in the high bearing capacity and the need to consider the replacement of large bearings; the overall stability of long-span steel truss arch bridges is weak, the structure of truss arch bridges is complex, and the design of rods requires full consideration of stability, etc.
Table 1 Length value of temperature section (m)
|
Structural Conditions |
Longitudinal temperature segment |
Transverse temperature region |
|
|
The capitals are Rigid joint |
The top of the column is hinged |
||
|
Heated houses and houses in non-heated areas |
220 |
120 |
150 |
|
Thermal workshop and heating area non-heating house |
180 |
100 |
125 |
|
open steel structure |
120 |
– |
– |
In recent years, various types of large-span spatial structures have developed rapidly in developed countries such as Europe and the United States. Buildings use a variety of new technology materials, and many characteristic large-span buildings have become local symbolic signs. Large-span space structures adopt various structural forms, and tension structures such as suspension cable structures and membrane structures are widely used. The research on the long-span spatial structure is developing rapidly in developed countries, and the structure is complex. In recent years, the research on large-span spatial structures in China has developed rapidly, and a large number of convention and exhibition centers have been built, which shows that the technical level of domestic spatial structure construction is relatively high. Table 1 shows the length values of different structural temperature sections. The arched structure is a unique structural form, and thermal stress is an important issue in the design of large-span steel structures. Most of the temperature effect research are aimed at concrete structures. There are few temperature effects of steel structures. Under the action of temperature, the structure will deform, and the deformation will be constrained to cause the structure to generate internal force.
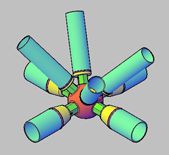
At present, the spatial structure design usually does not consider the influence of temperature-generated stress on the mechanical properties of the structure. The temperature difference causes the expansion and contraction of the spatial structure rods. Due to the deformation of the rods, temperature stress is generated. The construction in the northern region is concentrated in summer, and thermal expansion and cold contraction are common characteristics of buildings. The large-span steel structure produces thermal stress under the temperature load such as sudden cooling, which leads to the cracking of the structure. Since the 1960s, a large number of cracking accidents caused by thermal stress have occurred at home and abroad. Due to changes in the natural environment, temperature effects are divided into seasonal temperature differences and sunshine temperature differences. The temperature change is the premise of the temperature stress, and the temperature stress is essentially the temperature change stress. In a statically indeterminate structure, the temperature of the components changes linearly along the section height, and there is no temperature self-force. The temperature change in the statically indeterminate structure causes the deformation of the structure, resulting in thermal stress in the structure. The influence of construction on the service state is usually not considered in the structural design of the building. The deformation of the installation members of the large-span steel structure will affect the subsequent assembly. If the influence of the construction load is not considered, there will be potential safety hazards. In the construction of a large number of large-span buildings in my country, such as the Tianjin Natural History Museum, manual simulation analysis of the structure must be carried out. The large-span steel structure is a statically indeterminate structure, and the stress and deformation of the members will be caused by the temperature effect. In the construction of large-span steel structures, the structure is randomly affected by temperature, and the temperature in the construction of the structure may be any value. The shape of the structure is adjusted according to the temperature change. The structural deformation caused by the construction temperature change will cause residual stress. 50°C can cause a 163.3MPa temperature stress of the hinged rods at both ends. The temperature residual stress at the completion of the structure is an important issue of service stress. At present, there are few studies on the effect of temperature at home and abroad, focusing on the simulation analysis of bridge structures and the influence of temperature on the service period of the structure. It is necessary to simulate and analyze the construction temperature effect of the reticulated shell structure to provide a reference for the structural design.
 The research shows that with the increase of the thickness of the space frame, the compressive stress decreases, and the change of the thickness of the space frame has a great influence on the maximum temperature tensile stress of the chord. With the increase of the span of the space frame, the maximum temperature tensile and compressive stress of the web members increases gradually. The change in the span of the space frame has a great influence on the maximum deflection, and a small influence on the maximum temperature tensile stress of the chord. With the increase of the outer diameter of the space frame column, the maximum temperature tensile and compressive stress of the chord increases. The change outside the space frame column has a great influence on the maximum temperature tensile and compressive stress of the chord. The maximum tensile and compressive stress of the chord increases gradually, and the change of the outer diameter of the chord of the space frame has a great influence on the maximum temperature of the tensile and compressive stress of the web. . With the increase of stiffness, the temperature stress of the web rod increases slowly at a certain stiffness, and with the increase of stiffness, the maximum deflection increases to a certain stiffness. With the increase of stiffness, the increase of maximum deflection slows down, and the change of any factor has little effect on the temperature stress of the chord.
The research shows that with the increase of the thickness of the space frame, the compressive stress decreases, and the change of the thickness of the space frame has a great influence on the maximum temperature tensile stress of the chord. With the increase of the span of the space frame, the maximum temperature tensile and compressive stress of the web members increases gradually. The change in the span of the space frame has a great influence on the maximum deflection, and a small influence on the maximum temperature tensile stress of the chord. With the increase of the outer diameter of the space frame column, the maximum temperature tensile and compressive stress of the chord increases. The change outside the space frame column has a great influence on the maximum temperature tensile and compressive stress of the chord. The maximum tensile and compressive stress of the chord increases gradually, and the change of the outer diameter of the chord of the space frame has a great influence on the maximum temperature of the tensile and compressive stress of the web. . With the increase of stiffness, the temperature stress of the web rod increases slowly at a certain stiffness, and with the increase of stiffness, the maximum deflection increases to a certain stiffness. With the increase of stiffness, the increase of maximum deflection slows down, and the change of any factor has little effect on the temperature stress of the chord.







 About Us
About Us 2022-12-07
2022-12-07


