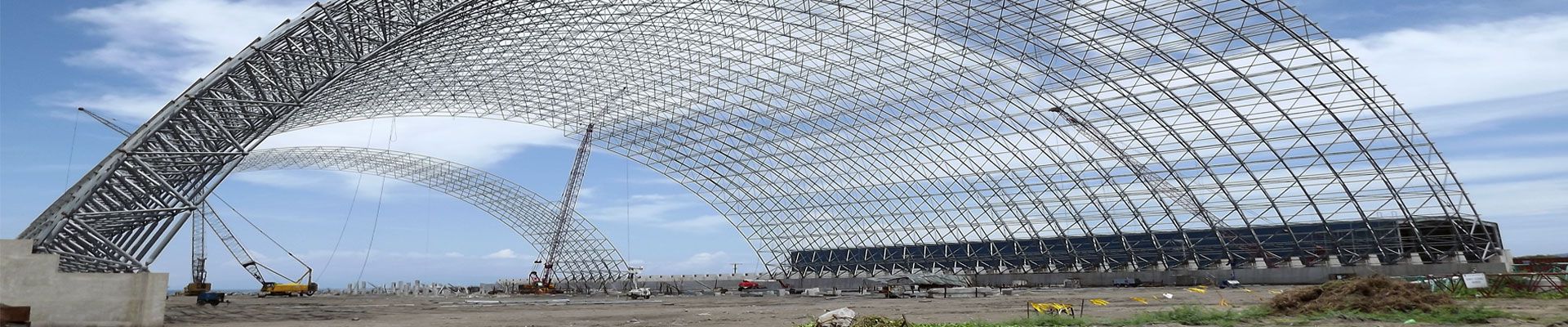
The choice of structural steel material is a critical aspect of construction that affects the structural integrity, durability and cost-effectiveness of a building. Proper steel selection includes understanding the different types and grades of steel, the processing methods used, and the coatings needed to prevent corrosion and rust. In this article, we explore the key skills needed to select structural steel materials.
Determine the type of steel you need:The two main types of steel used in construction are carbon steel and stainless steel. Carbon steel is strong, durable, and cost-effective, while stainless steel is highly corrosion-resistant and has a sleeker appearance.
Consider the grade of steel: There are several grades of steel, each with unique properties that make them suitable for different applications. For example, high-strength low-alloy steel is ideal for buildings that require greater strength and durability, while weathering steel is suitable for structures that are exposed to severe weather conditions.
Assess the thickness of steel: The thickness of steel affects its strength, weight and cost. Thicker steel has greater strength but is heavier and more expensive, while thinner steel is lighter and cheaper but may sacrifice some strength. When choosing a steel thickness, engineers must consider load-bearing requirements and cost implications. For example, in earthquake-prone areas, thicker steel may be required to withstand seismic forces.
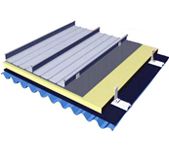
Analyzing coating options: Steel structures require protective coatings to prevent corrosion and rust. Common coating options include galvanizing, paint systems, and powder coating. Each coating option offers a different level of protection and aesthetic appeal.
Consider fire resistance: Steel is inherently fire resistant, but it still loses strength at high temperatures. Consider using fire-resistant coatings or fire-resistant materials to increase the fire resistance of steel structures , which need to be designed to meet fire safety standards. A variety of fire protection materials can be applied to steel structures to increase their fire resistance, including intumescent coatings, mineral wool and other sprayed products.
Check material availability and cost: The steel selected must be readily available and reasonably priced to ensure the project stays within budget and schedule , harder to obtain or more expensive materials can delay construction and increase project costs.
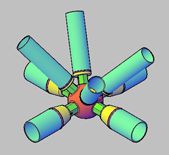
Processing methods : Processing methods such as tempering and forming can affect the final properties of the steel. For example, tempering involves heat treating steel to increase its toughness and strength. Forming processes include cold forming, thermoforming and welding. Welding steels with a carbon content above 0.3% requires special treatment to prevent cracking. Alternatively, mild steel is easy to weld but not suitable for highly stressed structures.
In conclusion, selecting the proper material for steel structures requires a thorough understanding of the different types, grades, thicknesses, coatings, refractory options, processing methods and cost implications. By following these skills, engineers and contractors can ensure the successful selection and implementation of steel for projects.







 About Us
About Us 2024-09-06
2024-09-06


