Structural safety
1.Load bearing capacity
Constant load: The weight of the glass roof itself is relatively large, especially in the case of thick glass or multi-layer glass combination. It is necessary to precisely calculate the self-weight of the glass, frame and connecting components, etc., and consider its long-term effect on the space frame structure. For example, the weight per unit area of different thicknesses and types of glass (e.g. tempered glass, laminated glass, etc.) is different, and the constant load needs to be calculated accurately according to the actual glass selected.
Live load: to consider the various live loads that may be subjected to. Including personnel maintenance, cleaning and other activities generated by the load, generally in accordance with a certain standard value of the live load (such as maintenance load take 1.0kN/m² or so) for the design. At the same time, the snow load should also be considered, which is particularly important for buildings in cold regions. The distribution of snow on glass roofs may not be uniform, and it is easy to form localized accumulations. Unfavorable snow load distribution needs to be considered to ensure that the mesh frame structure and glass roofs can carry the load safely.
Wind load: Wind load is a critical factor as the building roof is directly exposed to the outdoor environment. The shape, height and surrounding environment of the glass roof will affect the size and distribution of the wind load. For irregularly shaped glass roofs, complex wind pressure distributions may occur, such as larger negative pressures may occur at roof edges and corners. In the design of the wind tunnel test or refer to the relevant norms of the wind load body type coefficient to accurately calculate the wind load, to ensure the stability of the roof in the strong wind.

2.Connection node design
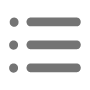
The connection node between the glass and the space frame structure is the key to ensure the safety of the roof structure. Node design should be able to effectively transfer the various loads borne by the glass to the space frame structure. For the use of point-type support glass roof, the strength and stiffness of the claw is critical. The claws need to use high-strength stainless steel materials, and through reasonable structural design to ensure that it can withstand the glass from the tension, pressure and shear.
The sealant between the glass and the frame is also an important part of the connection. Sealant should not only play a role in sealing and waterproofing, but also to a certain extent to withstand the relative displacement between the glass and the frame. In the design should consider the sealant bond strength, modulus of elasticity and other performance indicators, to ensure that it will not fail in the long-term use process, to ensure the reliability of the connection between the glass and the frame.
Waterproof drainage
1.Waterproof design
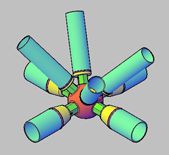
Glass gap waterproofing: the gap between the glass is the key part of waterproofing. Generally use sealant for waterproofing, to choose a good quality, weatherproof sealant. For example, silicone sealant has excellent weather resistance, water resistance and adhesion, is a common material for glass roof waterproofing. The construction quality of the sealant is also very critical to ensure that the seams are filled with full, even, to avoid bubbles, cracks and other defects, to prevent rainwater leakage.

Overall roof waterproofing: In addition to the glass seams, the overall waterproofing of the roof also needs to be considered. Glass roof and surrounding walls, daughter walls and other intersections of waterproofing treatment should pay special attention. Waterproofing membrane, waterproof coating and other materials can be used in conjunction with the glass roof sealant to form a complete waterproofing system. For example, in the roof and wall junction first laid waterproofing membrane, and then in the coil surface and glass junction and then play sealant, enhance the waterproof effect.
2.Drainage design
Drainage slope setting: in order to ensure that rainwater can be discharged smoothly, the glass roof needs to set a certain drainage slope. Drainage slope is generally not less than 2% – 3%. For the larger glass roof, you can use double slope drainage, four slope drainage and so on. The direction and size of the drainage slope should be based on the shape of the roof, structural form and drainage conditions around the building and other factors to determine.
Drainage system selection: drainage can be divided into organized drainage and unorganized drainage. Organized drainage includes rainwater pipe drainage and gutter drainage. Rainwater drainage is suitable for small glass roofs, the location and number of rainwater pipes should be reasonably arranged to ensure that rainwater can be collected and discharged in a timely manner. Gutter drainage is suitable for large glass roofs, the size, material and slope of the gutter should be designed according to the amount of roof catchment. For example, the use of stainless steel gutter, its width and depth to meet the drainage requirements, and to ensure that the gutter connection is well sealed to prevent water leakage.







 About Us
About Us 2025-04-04
2025-04-04


