
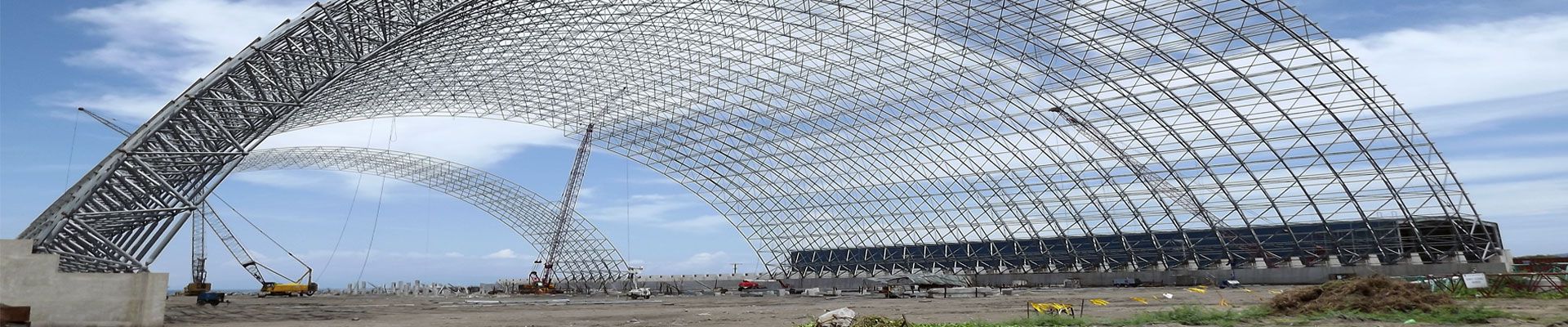
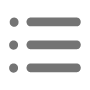
In the field of construction engineering, steel structure refers to a kind of engineering structure formed after processing, installation, and connection. It can withstand the influence of various natural environmental factors and man-made environmental factors, meet the various predetermined functional requirements of construction engineering, and has strong reliability and good social and economic benefits. The characteristics of steel structure are mainly reflected in its impact resistance, rapid construction and seismic performance, but its structural fire resistance is poor, and it is easy to rust. The most important thing is that the steel structure must be carefully designed and carefully constructed in the specific application process, so as to give full play to its advantages, so that the designed building structure can have enough reliability, and on this basis, achieve the maximum balance with social and economic benefits. In addition, the key to the design of the steel structure lies in the scheme selection. The specific content of the design scheme should include the type of steel structure, joint type, and connection mode. Among them, the choice of steel types and properties has very important practical significance, because the characteristics of steel structure and plastic size, and toughness is good or bad there is a direct relationship. That is to say, according to the characteristics of the steel structure design requirements to choose the structural steel in line with it.
1. Main types of steel in steel structure
1.1 Carbon structural steel
Under normal conditions, the grade of carbon structural steel can be divided into five grades according to the carbon content and yield strength, which are Q195, Q215A, BQ235A, Q225A, and Q275, where Q represents the yield strength, and generally N/mm² is used as a unit to represent the size of yield strength. ABCD stands for the level of quality division. In the final pouring process, because of the different degrees of deoxidation, different types of steel are also divided into calming steel, plate calming steel, and boiling steel types. Q195 to Q275 are arranged using the intensity level. Moreover, the strength of steel is mainly determined by the number of carbon elements contained in it, and is also related to other elements and content. Therefore, the steel number represents the level of carbon content to a certain extent. Among them, the light of Q195 and Q215 is relatively low, and the upper limit of the carbon content of Q225 is beyond the standard range of low carbon steel, so the main application of building structure in carbon steel structure is Q235 this model. The quality grading in the steel number is mainly from A-D, which represents the quality from low to high. The quality is mainly based on the impact toughness to distinguish, the requirements for cold bending test are also different. For A-grade steel materials, there is no obvious requirement for impact toughness. In the cold bending test, it only needs to be carried out when the demand side requires it. However, the three grades of BCD all require the AKV value of impact toughness to be no less than 27J, but the test temperature of the three is also different. In order to meet different performance requirements, different grades of Q235 steel chemical element content is also different.
1.2 Low alloy steel
The formation of low alloy steel is mainly to add a variety of alloy elements to ordinary carbon steel. When the total amount is less than 5%, it is called low alloy steel, and when it is more than 5%, it is called high alloy steel. If only low alloy steel is used in the building structure, its yield point and tensile strength are much higher than carbon steel, and it has strong plasticity and impact toughness, and it also has good resistance to corrosion. According to the relevant regulations of our country, low-alloy and high-strength structural steel can be divided into five different types. The most common ones are Q355, Q390, and Q420. From the point of view of mechanical properties, these three grades are all composed of steel. In addition to grade A steel with different impact toughness, the rest of the grades ensure a number of indicators such as cold bending, impact toughness, and elongation.
2. Main properties of steel

2.1 Strength
The strength index of steel materials is mainly based on the tensile limit, elastic limit, and yield limit. The higher yield strength can reduce the deadweight of the structure, save steel materials to the maximum extent, and reduce construction cost. The tensile strength refers to the maximum stress that the steel can withstand before being damaged. In this process, the steel structure will lose its service performance due to the large plastic deformation, but the structural deformation does not represent the overall structure down, which means that the steel material structure can meet the seismic design requirements.
2.2 Plasticity
Steel plasticity generally refers to the property of having significant plastic deformation without fracture after the stress exceeds the yield critical value. The key indicators for judging the plastic deformation ability of steel are elongation and reduction of area.
2.3 Cold bendability
The cold bending properties of steel materials can be used to judge the crack resistance of steel materials caused by plastic deformation during bending processing at room temperature. When testing the deformation performance of steel to withstand a specified degree of bending, it mainly relies on the cold bending experiment of cold bending performance.
2.4 Impact toughness
Under a certain load, the impact toughness of steel can be fully reflected. At the same time, it is also an important ability to absorb mechanical kinetic energy during the fracture process, and it is also an important standard to measure the impact resistance of steel. In addition, under normal circumstances, the impact test of standard specimens is used to obtain the impact toughness index data of steel.
2.5 Weldability
Welding properties of steel materials usually refer to materials that can obtain good welding properties under certain welding process conditions. Welding performance is divided into two types, namely welding performance in welding and in use. In the specific steel welding process, the welding performance mainly refers to the sensitivity that the weld seam and the metal around the weld seam will not produce hot cracks during the welding process, or the sensitivity of cooling shrinkage cracks will not occur under cooling conditions. The general judgment of performance is mainly to see whether there will be cracks between the weld metal and the nearby base metal under certain welding process conditions. Welding performance in terms of performance refers to the impact toughness at the weld and the ductility of the heat-affected zone. In this process, the mechanical properties of the weld and the steel within the heat-affected area must not be weaker than the base metal.
2.6 Chemical properties
The chemical properties are divided into three points: corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance and chemical stability. Among them, corrosion resistance refers to the ability of metal materials to resist the corrosion of the surrounding medium. The corrosion resistance of steel is related to many factors, such as metal chemical composition, heating properties and heat treatment conditions, etc. Oxidation resistance refers to the ability of steel to resist oxidation at room temperature or high temperature. The metal oxidation process is actually another form of chemical corrosion. It can be directly applied in a specific time, and the loss after the metal surface is corroded can be expressed by the metal weight loss speed. Finally, chemical stability is the general term for the first two properties of metal materials, that is, the thermal stability of steel under high temperature conditions.
3 Selection principles of steel in steel structure engineering
3.1 Select according to the purpose
In order to achieve the goal of saving energy, steel structures must always follow the principles of high performance and high safety in the process of steel selection. According to the actual characteristics of steel structures, important projects such as bridge engineering, high-rise building engineering structures, and large stadium structures, All need to choose the steel type specially made by the steel factory.
3.2 Taking into account other influencing factors
From the point of view of the importance of steel structures, different types of steel structures can be divided into three levels, which are important, common and secondary. Some important building structures should use higher-grade steel. Due to the large temperature difference between the north and the south of our country, and the large temperature difference between winter and summer, it is necessary to use grade D or above steel to give full play to the low-temperature toughness of minus 20°C. In the manufacturing process of steel bridges, the volume of individual components is very large, and the shape and structure are very complicated. It is impossible to heat treat the whole body. It is necessary to select hot-rolled or normalized, quenched and tempered steel types for direct production. Bridge steel structures usually adopt cold bending and welding manufacturing processes, which require the metal materials to have low timeliness and maintain excellent performance. Since bridge structures are often exposed to outdoor environments, steel materials are required to have good low-temperature toughness and weather resistance. And the bridge structure has been subjected to dynamic loads for a long time, so the steel must have excellent strength, plasticity and impact toughness.
3.3 Quality grade selection
In terms of quality grade, A-grade steel is usually used, while welded structures and static load structures need to use B-type steel, and in the dynamic load, it is necessary to combine the temperature of the environment where the steel structure is located, and reasonably select C, D, E For special-grade steel, it must be ensured that the brittle transition temperature of the steel is lower than the ambient temperature. At the same time, for heavy-duty welded steel structures with complex joint structures and harsh working environments, strict requirements for steel quality standards are also required. In addition, the quality level of important steel structures should also be appropriately improved.
3.4 Strength grade selection
If it is an ordinary steel structure in a construction project, the strength grade of the steel material should usually be Q235 and Q355, or special steel with a higher strength grade. However, if it is an ultra-light steel structure or a color-coated panel on the wall, it is necessary to choose steel with a strength grade of Q235 and Q355. In the lock seam connection process, it must have good cold bending performance, and if necessary, a multi-layer roll flattening non-damage test can be carried out. In addition, in the crimp connection, it is necessary to choose steel with better toughness.
With the rapid development of my country’s economic construction and the continuous increase of steel production, steel is widely used in plant structures, plate and shell structures and large-scale building facilities structures due to its high strength, lightweight, high rigidity, and excellent toughness. It will occupy a very important position in the construction industry. At the same time, as a structure mainly made of steel materials, the selection of high-quality and durable steel materials during the construction period of the steel structure plays a vital role in promoting the development of steel structure buildings.







 About Us
About Us 2023-03-17
2023-03-17


