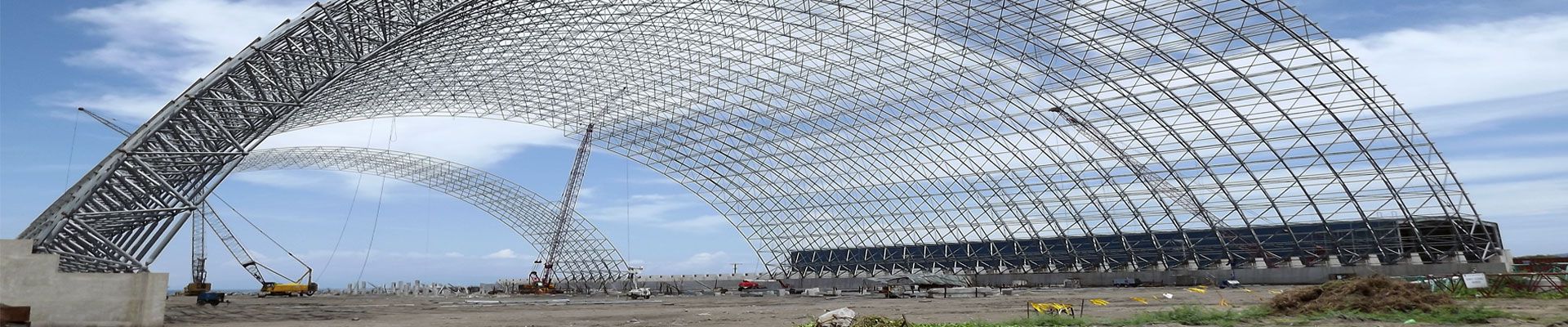
1.Summary
The reason for the wide application and rapid development of space frame structure is that in addition to its rational force and economic practicality, its changeable shape can give architects rich imagination and broad design space. Similarly, place oneself in the large industrial plant, the roof space frame structure with its regular space frame, full of three-dimensional sense is put four cone combination, can let a person feel pleasing to the eye. This kind of roof form and function of harmony and unity, is ordinary steel structure roof can not achieve, therefore, the space frame structure form is more and more favored by architects. The automobile oil shed in the oil depot adopts the space frame structure, and the space frame structure is designed and constructed directly by the manufacturer in the tradition. Aiming at the gap in this aspect of the space frame structure in our company, this paper summarizes the design points of the space frame structure for design reference.
2.Space framestructure
In the classification of space frame structure, different classification methods can be used to classify different types of space frame structure. They can be classified as follows:
2.1 Classification according to supporting conditions
2.1.1 Peripheral Supporting Space Frame Peripheral Supporting
space frame is a form that is widely used at present. All boundary nodes are placed on columns or beams, with direct force transmission and uniform force on the space frame frame. When the periphery of the space frame is supported on the top of the column, the space frame width can be consistent with the column distance. When the space frame is supported on the ring beam, the mesh division is more flexible and can not be affected by the column distance.
2.1.2 Point support Space Frame
Generally, there are two kinds of four-point support and multi-point support. Because of the large concentrated force at the supporting points, it is appropriate to set up cantilevers around the perimeter to reduce the internal force and deflection of the mid-span members of the space frame.
2.1.3 space frame with point support in the point support space frame, when there is no envelope structure and wind resistance column around, the form of combining point support and surrounding support can be adopted. This support method is suitable for public buildings such as industrial plants and exhibition halls.
2.1.4 Truss with three sides supporting one side opening or two sides supporting two sides opening
In a rectangular plane building, due to the possibility of expansion or the requirements of the building function, it is necessary to open on one side or two pairs of sides, so that the space frame is only supported on three sides or two pairs of sides, and the other side or two pairs of sides is a free edge. The existence of free edges is disadvantageous to the force of the space frame, so special treatment should be made for the free edges. Can be added near the free edge of the net layer or in the free edge of the joist or bracket. For medium and small space frames, it can also be strengthened by increasing the height of space frames or enlarging the section of bars locally.
2.2 Classification by space frame form
This is the most commonly used classification of the space frame structure, according to the “Rules for the design and construction of the space frame structure” JGJ7-91, we often use the space frame structure is divided into four systems and thirteen types of space frame structure.
2.2.1 Cross-plane truss system
The space frame structure of this system is composed of some intersecting plane trusses. Generally, the oblique ventral rod should be pulled and the vertical rod under pressure. The angle between the oblique ventral rod and the chord rod should be between 40 º and 60º. The system has the following four types of space frame:
2.2.1.1 Two – way orthogonal forward frame
Two orthogonal forward laying space frame is composed of two sets of plane trusses intersecting each other 90º, and the chord rod is parallel or perpendicular to the boundary. The space frame size of the upper and lower chords is the same, and the length of the plane trusses in the same direction is the same, which is easy to make and install. Because the upper and lower chords are square space frames and belong to a geometrically variable system, the horizontal support of the upper and lower chords should be properly set to ensure the geometric invariance of the structure and effectively transfer the horizontal load.
2.2.1.2 Two – way orthogonal oblique space frame
The two-way orthogonal diagonal laying space frame is composed of two groups of plane trusses intersecting each other 90º, and the chord rod and the boundary form 45º Angle. When the boundary is reliable, it is geometrically invariant. The lengths of trusses are different, and the stiffness of the short trusses near the corner is larger than that of the long trusses perpendicular to it, which has an elastic support effect on the long trusses perpendicular to it, and can reduce the positive bending moment in the middle of the long trusses, so it is more economical than that of the orthogonal forward truss. However, due to the negative bending moment at both ends of the long truss, the four-angle support will produce a large tension. The angular tension shall be borne by the two supports.
2.2.1.3 Two – way oblique oblique space frame
The diagonal diagonal laying space frame is formed by two sets of plane trusses intersecting obliquely, and the chord rod forms an oblique Angle with the boundary. This kind of space frame structure is more complex in space frame layout, construction, calculation and analysis, production and installation, and the mechanical performance is also relatively poor, except for special circumstances, generally should not be used.
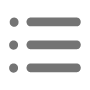
3. Structural design of space framestructure
The main dimensions of the space frame structure are the space frame size (refers to the chord space frame size) and the height of the space frame. These dimensions should be determined considering factors such as span size, column mesh size, roofing material, structural requirements and building function.
3.1 space frame size The size of the space frame directly affects the economy of the space frame. When determining the mesh size, it depends on the following conditions:
3.1.1 Roofing materials
When the roof adopts no purlin system (reinforced concrete roof slab, steel wire space frame cement slab), the mesh size is generally 2 ~ 4m. If the mesh size is too large, the weight of the roof board is large, not only increases the load of the space frame, but also makes the lifting of the roof board difficult. When steel purlin roofing system is used, purlin length should not exceed 6m. The mesh dimensions shall be suitable for the above roofing materials. When the mesh size is greater than 6m, the diagonal rod should be divided again, and attention should be paid to ensure the stability of the rod.
3.1.2 The space frame size shall be proportional to the height of the space frame
Usually, the Angle between the oblique belly rod and the chord rod should be 45º ~ 60º, so that the joint construction will not be difficult.
3.1.3 Steel specifications
The space frame size can be larger when the reasonable steel pipe is used as the space frame. The space frame size should be smaller when using angle steel bars or only smaller steel.







 About Us
About Us 2024-10-24
2024-10-24


