The selection of space frame should be combined with the plan shape of the building, requirements, load, and span size, support situation, and economic factors such as comprehensive consideration. Usually, we divide it according to the span size as follows: above 60m span is a large; 30m to 60m is a medium span; below 30m is a small span.
Planar truss system
1. Two-way orthogonal upright space frame
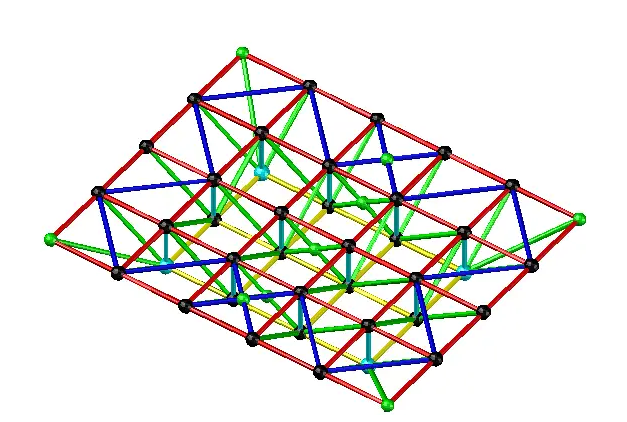
Structural characteristics: geometrically variable in plane. To increase its spatial stiffness and effectively transfer horizontal loads, additional diagonal rods should be set up in the upper (lower) chord plane along the perimeter of the space frame support. The peripheral support is close to the square plane, the force is uniform, and the difference in the internal force of the rods is not big. With the increase in side length ratio, the unidirectional force characteristic is obvious. For the point bearing space frame, the internal force of the rods near the bearing and the chord in the the main truss span is large, while the internal force in other parts is small.
Application: rectangular plane, peripheral support, side length ratio less than 1.5, various spans can be used.
2. Two directional orthogonal diagonal space frame
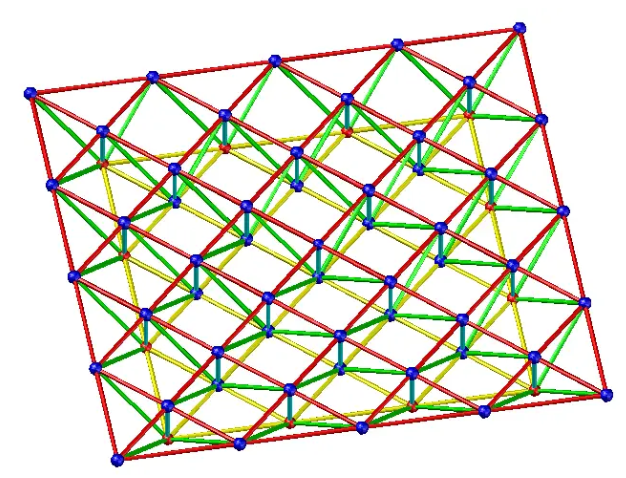
Structural Characteristics: Since the space frame is of equal height, the short truss at the corner has greater rigidity and plays a certain elastic supporting role for the long truss which is perpendicular to it, thus reducing the bending moment in the middle of the truss. The perpendicular long truss plays a certain elastic supporting role, thus reducing the bending moment in the middle of the truss. The stiffness is larger than that of two-way orthotropic orthotopic space frame. In rectangular plane, the force is more uniform. There is upward tension at the corner supports of the space frame.
Application:rectangular plane, peripheral support, side length ratio less than 1.5, various spans can be used.
3.Unidirectional folded wire space frame
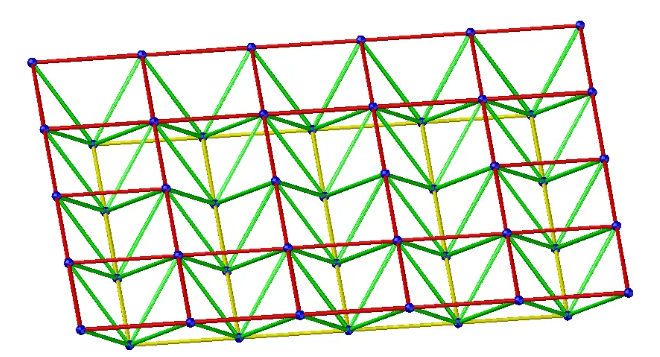
Structural Characteristics: Similar to three-dimensional truss, but without bracing system. There are only upper and lower chords along the span direction, which are in unidirectional stress state. In order to strengthen its spatial stiffness, part of the upper chord should be added in its periphery.
Application: Rectangular planes, peripheral support, side length ratios greater than 2.
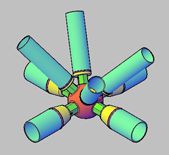
4.Three-way space frame
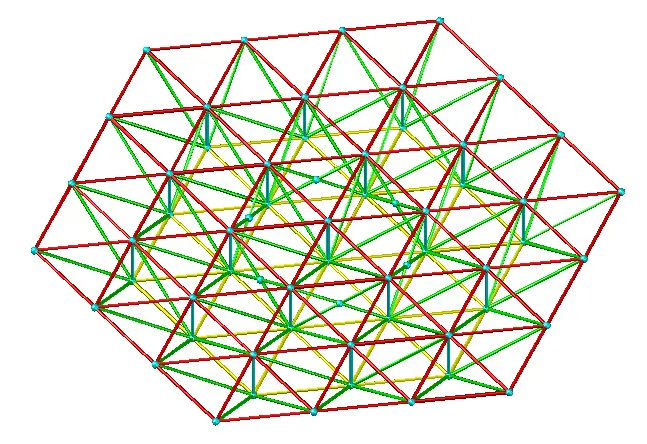
Structural characteristics: the basic unit is geometrically invariant. The spatial stiffness of the whole frame is greater than that of the two-way frame. The force can be uniformly transmitted to the supporting system, and the force performance is better. The number of rods and nodes is large, and the node structure is complicated (at most one node intersects 13 rods).
Application: For circular or polygonal planes with a regular space frame around the perimeter, suitable for large-span projects.







 About Us
About Us 2024-06-11
2024-06-11


