- Material selection:
Select materials suitable for intended use. Common materials include steel 45#, aluminium or other alloys depending on factors such as strength, corrosion resistance and weight.
- Raw material processing:
The selected material is usually procured in the form of raw material blanks or prefabricated parts. These raw materials may need to undergo preliminary processing steps such as cutting or machining to obtain more manageable dimensions.
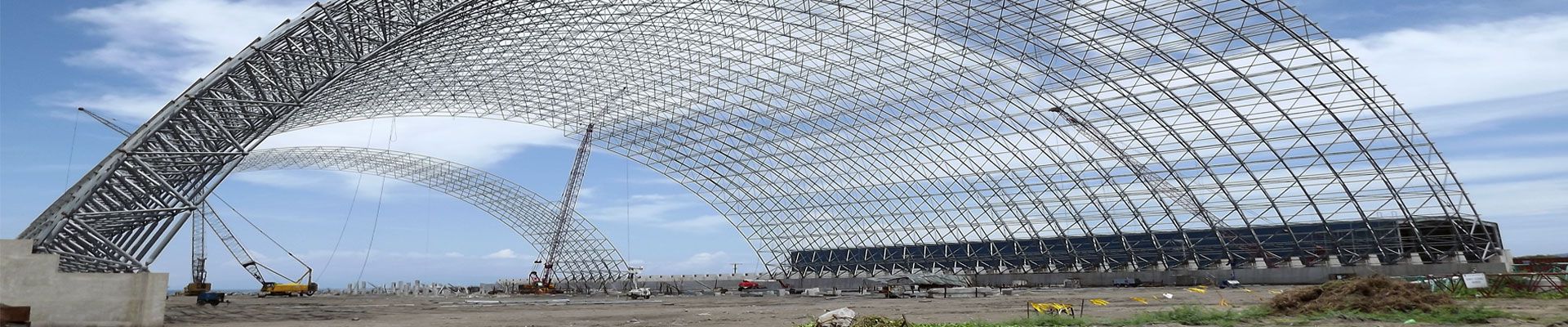
- Forming spheres:
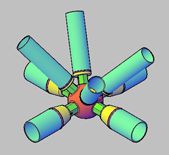
Materials can be shaped into spheres using the forging process, which uses compressive forces to shape the material.
- machining:
Precision machining processes such as turning or milling can be used to achieve the final dimensions and surface finish of a spherical part. This step ensures that the spheres are uniform and meet the required specifications.
- Heat treatment:
Depending on the material used, heat treatment processes can be used to improve the mechanical properties of the spherical parts. Heat treatment can increase hardness, strength and durability.
- surface treatment:
Surface treatments such as coatings or plating can be used to enhance corrosion resistance, improve aesthetics, or provide additional functional properties. For example, zinc coatings prevent rusting of steel balls.
- quality control:
Rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the production process. Inspections may include dimensional checks, surface quality assessments, and material performance tests to ensure that the steel balls meet industry standards.
- Packaging and Distribution:
Once the bolted balls have been manufactured and passed quality inspection, they will be packaged for shipment. Proper packaging helps prevent damage during transport and storage.
It is important to note that the exact process will vary depending on the size, material and intended use of the bolts. Manufacturers typically adhere to industry standards and specifications to produce components that meet the required performance criteria.







 About Us
About Us 2023-12-22
2023-12-22



