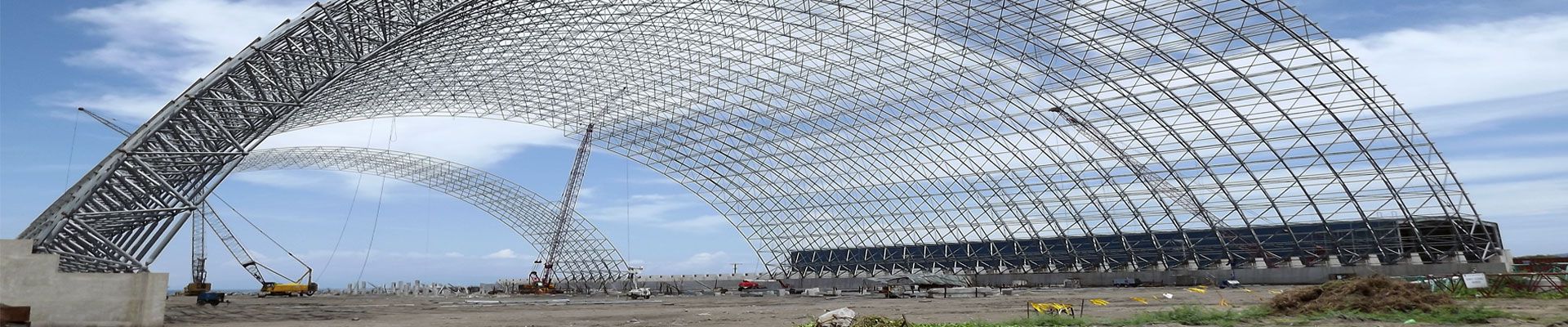
 The material used in the space frame processing needs to be guaranteed to be a good material to ensure the stability of the space frame, and it will not cause the construction of the space frame to fail as in meeting the required safety standards, but there are often some factors that affect the performance of the material, making it unable to meet the normal use.
The material used in the space frame processing needs to be guaranteed to be a good material to ensure the stability of the space frame, and it will not cause the construction of the space frame to fail as in meeting the required safety standards, but there are often some factors that affect the performance of the material, making it unable to meet the normal use.
- chemical composition
- Carbon: the main component that constitutes the strength of steel. As the carbon content increases, the strength of the steel increases, but at the same time the plasticity, resistance, cold bending function, weldability and corrosion resistance of the steel decreases, especially the impact resistance at low temperatures.
- Manganese and silicon: The beneficial elements in steel are all deoxidizers, which can increase the strength without excessively reducing plasticity and impact resistance.
- Vanadium, niobium, and titanium: alloying elements in steel, which can not only improve the strength of steel, but also maintain outstanding plasticity and resistance.
- Oxygen and nitrogen: there are impurities in steel. Oxygen can make steel hot and brittle, and nitrogen can make steel cold and brittle.
- Aluminium: A strong deoxidizer that uses aluminum to compensate for deoxidation, which can further reduce harmful oxides in steel.
- Chromium and nickel: alloying elements that improve the strength of steel.
- Sulfur and phosphorus: impurities left in the steel during the exercise, there are elements. They reduce the plasticity, durability, weldability and fatigue strength of the steel used for space frame processing. Sulfur can make steel “ hot brittle”, and phosphorous make steel “ cold brittle”. “ Hot brittleness”: Sulfur can produce iron sulfide which is easy to melt. When the temperature reaches 800-1000℃ by hot working and welding, it will make the steel crack and become brittle. “cold brittleness”: At low temperatures, phosphorus greatly reduces the impact resistance of steel.
- The influence of metallurgical defects.
Common metallurgical defects include segregation, non-metallic inclusion, pores, cracks, delamination, etc., which will make the steel processed by the space frame function worse.
- Steel hardening, cold drawing, cold bending, punching, mechanical shearing and other cold processing make the steel undergo great plastic deformation, and then increase the yield point of the steel, and reduce the plasticity and resistance of the steel. This appearance is called cold work Hardening or strain hardening.
- The influence of temperature: The steel processed by the space frame is appropriately sensitive to temperature, and the temperature rise and fall will cause the function of the steel to change. In contrast, the low temperature function of steel is more important. At the positive temperature scale, the general trend is that as the temperature increases, the strength of the steel decreases and the shape increases. The function of the steel does not change much within about 200℃, and the strength (yield strength and tensile strength) drops sharply between 430-540℃; when it reaches 600℃, the strength is very low and cannot bear the load. In addition, there is a blue and brittle appearance near 250℃, and a creep appearance at about 260-320℃. The factors that affect the processing materials of the space frame are mainly the above four points. Among them, special attention should be paid to the effect of temperature on it, because it is not only affected during the production and processing, but also the change in the external temperature after the construction is completed.







 About Us
About Us 2021-10-12
2021-10-12


