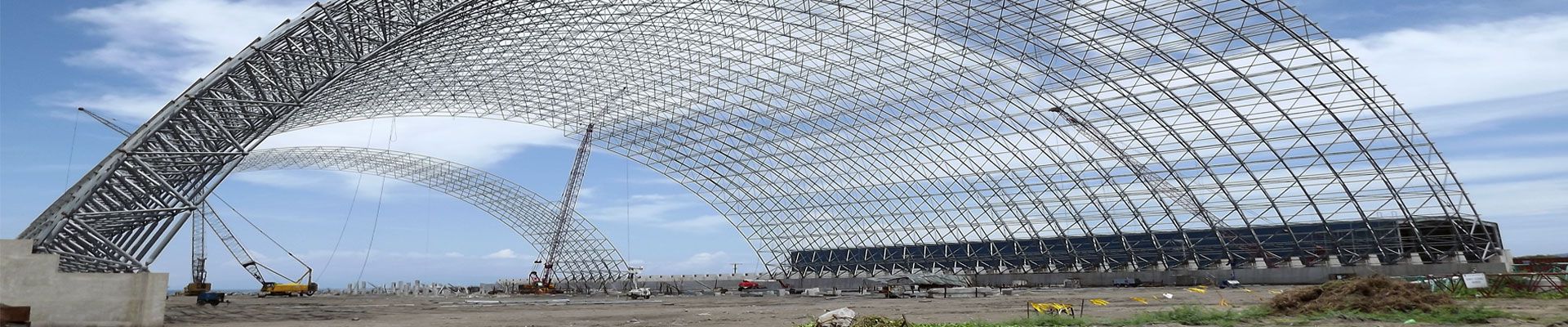
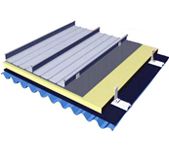
A glass skylight roof is a roofing system made from glass, typically constructed with a frame that supports the glass panes. Glass roofs are commonly used in commercial, residential, and public buildings. They are becoming increasingly popular in modern architecture due to their aesthetic appeal, ability to let in natural light, and energy–efficiency. Glass roofs can be made from single or double–glazed glass and can be tinted to reduce glare and regulate the amount of light and heat entering the building. Glass roofs are also popular in greenhouses, conservatories, and atriums.
Architecture is formed and developed with the development of productive forces under certain historical conditions. With different social and historical conditions and the development level of productive forces, people have different requirements for architecture and the methods to realize these requirements are also different. The glass skylight is an integral part of the building, and it develops with the development of the building. Therefore, to study the development of the glass skylight must study the development of the building. During the Qin and Han dynasties, the working people in our country created clay bricks and small clay tiles for building houses, using bricks for walls and tiles for roofs. Later, with the appearance of glass, people gradually used roofs for lighting. One way is to use glass to form glass arc tiles like small blue tiles by hot pressing. The disadvantage of this method is that the lighting area is small and can only be used between the rafters. Another way is to make a special lighting opening on the part of the roof that needs lighting and covers it with flat glass. This kind of lighting opening has a large lighting area, but the drainage method is complicated, the nodes are not handled well, and it is often prone to leakage.

In the late 19th century, with the process of world industrialization, a number of large-scale industrial factories sprang up. Some of these factories had a span of more than 30m. Daylighting by side windows alone could not meet the lighting needs of the factory buildings. Therefore, daylighting skylights came into being. The commonly used ones are lighting cover, lighting board, lighting belt, and triangular skylight. These skylights are mainly used for lighting and ventilation, and also have a decorative meaning. These skylights basically use steel (wooden) skeletons, and some glass is installed directly on the reinforced concrete frame or reinforced concrete slab.
In the 20th century, aluminum alloy profiles were used in building doors, windows, and curtain walls, and there were aluminum alloy glass lighting roofs. This new type of lighting roof has made a big leap in its status in architecture. Its geometric shapes include single slope, double slope, semicircle, 1/4 circle, broken line, cone, dome, etc., as well as these basic geometric shapes. Groups, conjoined bodies composed of shapes, and conjoined bodies formed with curtain walls. In the 1980s, with the widespread application of structural glazing technology, glass-lighting roof buildings were also made of structural glazing technology, and aluminum alloy hid frame glass-lighting roofs appeared. This type of lighting roof has no clamping glass on the upper surface of the glass. The upper surface of the glass top forms a flat surface so that the rainwater can flow down unimpeded. At the same time as the glass frame glass curtain wall was born, the glass frame glass daylighting roof appeared. The supporting frame and the daylighting panels are all made of glass. The new daylighting roof gives the glass daylighting roof a brand-new artistic image. Due to the unobstructed full view, it gives people a unique artistic enjoyment, and it has begun to be used in many public buildings.

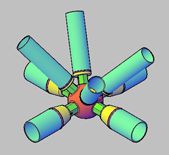
In recent years, the glass skylight has developed rapidly, especially the dotted glass skylight, which is popular among architects and owners for its simple shape, lightness, and beauty. Therefore, many excellent buildings in foreign countries are famous for their unique glass structure design, especially in Germany, the point bar glass lighting roof has a high level of development and wide application, for example, Augsburg (Augsburg) ) glass roof of the Maxim Museum and a glass roof of the Medieval Jewish Courtyard in Speyer. The common point of these two glass roof structures is that the designer adopts a reasonable structural form for the characteristics of high compressive strength and low tensile strength of the glass, so as to generate compressive stress in the glass as much as possible and reduce tensile stress. Such as the glass roof of the Maxim Museum. The glass roof of the museum is a cylindrical shell with a structure length of 37m, a span of 14m, and a height of 4.5m. The main stress is compressive stress, which is the mechanical characteristic of glass with good compressive performance. The structure is also composed of an indispensable prestressed steel cable system, which is divided into two groups. The first group is the radial cables arranged along the axis in the vertical plane of the structure. The longitudinal distance of each cable is 3.85m, and the interval is 4 For a piece of glass, the middle connecting cable is middle 12, and the rest are middle 10. The second group of steel cable systems is the middle 8 prestressed steel cables arranged diagonally in the plane of the glass plate. This group of steel cables ensures that when one or more pieces of glass are broken, the structure can still remain stable. Together the rigging strengthens the structural integrity. Another example of a glass structure in Speyer City consists of a glass roof and stainless steel supports. The main structure of the roof is a tensioned glass beam with a span of 9m. The beam is formed by connecting two parts at the top with a certain angle. Pressure along the axis of the beam will be generated. The glass beam is tempered laminated glass of 12mm+12mm. Both ends of the tensioned glass beams are connected to the glass side beams, the span of the glass side beams is 6m, and the span of the roof glass panels is 1.2m, which is 8mm+8mm semi-tempered glass. The glass components are mechanically connected and caulked with silicone. This kind of building has become a representative part of German architecture in the 1990s with modern architectural ideas and novel structural shapes. It is precise because of the efforts of German and European architects and engineers that the further development of glass structures in the world has been promoted.

Many representative point-supported glass skylight roof projects have appeared in China, such as the Nanjing Olympic Sports Center Gymnasium Curved Glass Roof, the Beijing Botanical Garden Plant Exhibition Greenhouse with a unique shape (Figure 4), Shenzhen Civic Center Glass Lighting Roof And the circular roof of the central hall with a diameter of 15m in Kunming Bolian Square. The glass daylighting roof of the Shenzhen Civic Center is built with a self-designed prestressed cable space frame. This structure combines the space frame structure technology with good spatial rigidity and the cable structure that can give full play to the tensile properties of steel through prestressing means. The technologies are organically integrated to form a new prestressed cable structure system. The circular roof of the central hall with a diameter of 15m in Kunming Bolian Plaza is the first stringed reticulated shell glass daylighting roof built in my country. The upper layer is covered with insulating glass. , the lower chord uses prestressed ring cables, the upper chord nodes are pulled by oblique cables, and the vertical connecting compression rods are used between the upper and lower chords. Although the glass skylight structure has certain engineering applications in my country, the engineering application of glass as a load-bearing component is still blank. Although it has a certain relationship with the country’s economic development level, the most important thing is that we started relatively late in the theoretical research of glass structure, and have not yet developed relevant design and analysis software, coupled with foreign technology secrecy and other reasons. , many key theoretical issues have yet to be studied by Chinese people.







 About Us
About Us 2023-03-08
2023-03-08


