1. Process flow
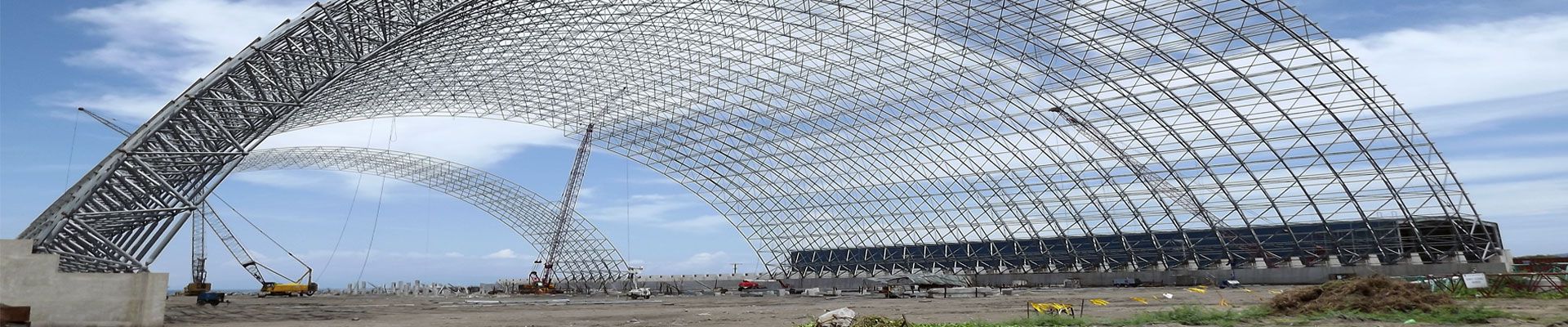
The pipe truss of this project is an inverted triangle with a span of 72m, a mid-span belly height of 4.5m, a top chord width of 3m, the top chord pipe is 4203×12 seamless steel pipe, the bottom chord is $377×10 seamless steel pipe, and the web rod is p114×5, 4140 × 6, 4159 × 6, 4159 × 8 steel pipes, all of which are Q355B. Due to the large span of the truss and inconvenient transportation, it is adopted assembled on the construction site as a whole, and then hoisted as a whole. Pipe truss production is divided into tire frame production, steel pipe intersecting cutting and pipe truss assembly and welding. All pipe components are cut in the workshop by CNC five-dimensional intersecting wire-cutting machine and then transported to the construction site for assembly after derusting and painting.
2. Introduction to construction technology
In order to ensure the overall dimensions of the components when they are assembled, the assembled tire frame must be set in strict accordance with the design dimensions. The tire frame is placed on the compacted ground, and the surface is leveled by a steel backing plate.
2.1 A retest of the tire frame
(1)Contents of the retest: including positioning coordinates, design form of the tire frame, material of the tire frame, etc.
(2)The meaning of re-measurement: the accuracy of the assembled rod is realized by the accuracy of the tire frame, so the accuracy of the tire frame must be accurate.
2.2 Acceptance and preparation of components
(1)Matching of components.
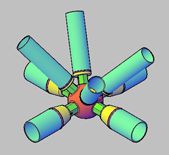
The rods must be matched, and at the same time, the rods must be placed within the working radius of the crane. After the on-site assembly of the steel pipe is verified on the tire frame, it is fixed by temporary connection lugs, and finally welded. The positioning accuracy of the chord is very critical, and only after accurate measurement can it be positioned with a fixture. Spot welding positioning is strictly prohibited, especially the lower chord. On the chord, fix the point of the web rod to achieve “one line and two points”. The line refers to the intersecting line of the surface where the axis of the web rod is located and the surface of the chord rod, and the two points refer to the toe point of the end of each web rod. with heel point. When the upper chord is in place, use the 476×5 steel pipe diagonal brace to support the upper chord as the fulcrum, and then manually adjust the temporary brace to the corresponding position before the crane can remove the hook. Each truss is provided with 7 groups of temporary braces, 2 in each group. The position of the temporary strut avoids the intersecting position of the web between the upper and lower chords. Due to the inverted splicing method and the larger web height of the truss, it is more difficult to assemble the web bars between the upper and lower chords. Therefore, it is necessary to use a hoist to pull the web bars to the specified height and then assemble the fixed point. Remove the temporary support after the web bar is assembled.
(2)The key issues that should be paid attention to in the assembly process.
Since the end of the truss needs to be connected with other trusses, if the size is out of tolerance, it is bound to cause great difficulty in installation. In the intersecting node, the axes of each branch pipe must intersect at one point. In this way, the occurrence of additional torque at the node can be avoided, which is more conducive to the safety of the structure.
2.3 Intersect welding
(1)Welding essentials. Choose appropriate welding materials; choose appropriate welding methods; choose appropriate welding parameters; do welding process qualification first; preheat according to regulations before welding;
(2)Welding method. Welding by manual arc welding and gas-shielded welding.
(3)Welding materials. Since the steel is Q355, the E5015 and E5016 low hydrogen electrodes of the E50 series are selected for welding.
(4)Welding procedure evaluation. Welding procedure qualification shall be based on reliable welding performance. Welding procedure qualification verifies the correctness of the welding procedure formulated by the construction unit and evaluates the ability of the trial welding unit. The equipment and instruments used in the welding procedure evaluation should be in normal working condition, the steel and welding materials must meet the corresponding standards, and the welding personnel who are skilled in welding the unit should use the welding equipment of the unit to weld the test piece.

(5)Preheating before welding and post-heating after welding. The preheating temperature before welding is 120-130°C, the interpass temperature is 120~200°C, the preheating range is not less than 3 times the width of the weld and not less than 100mm, and the post-heating temperature is 250°C immediately after the welding is completed. Constant temperature for 2h, then slow cooling, heating by electric heating, and automatic temperature control.
(6)The residual stress is eliminated by hitting with a small hammer. The hammer height should not exceed 3cm, 100 times per minute, the hammering density should be 15~20 times/cm, and the constant temperature during hammering should not be lower than the preheating temperature.
(7)Nondestructive testing of welds. The welding seam form of the joint part of the pipe truss is complex, and the welding position is changeable. For a through hole, there are three welding positions: flat, vertical, and inclined, and three groove angles. Therefore, there are many factors affecting the welding quality, and strict testing measures must be taken to ensure the welding quality.
2.4 Steel pipe truss hoisting
The pipe truss is hoisted by a double machine and a single truss. The crane stations are 4.5m outside the span on both sides, and they are hoisted in sequence.
(1)Preparation before hoisting.
The hoisting of the pipe truss should be carried out after the installation and correction of the steel column and its supports are completed. Since the second grouting of the column base has not been completed, in order to prevent the anchor bolts from becoming unstable during the installation of the truss, before lifting, 8 pieces of wedge iron are hit under each steel column base plate.
(2)Turn over (straighten up).
The pipe truss is upside down and must be turned over when hoisting. When turning over, two 50t cranes operate at the same time. According to the actual situation on site, a 25t truck crane is used to assist in turning over. The lifting body is 4~7m away from the truss, and the lifting point is located in the center of the tube truss. Before straightening, pad points (sleepers) should be set at both ends of the pipe truss or at the lower chord node, so that it can be placed on it after straightening.
(3)Lifting.
The pipe truss is hoisted by a double machine. When the double machine is hoisted, the pipe truss is located in the middle of the span, and two cranes stand on the outer sides of the span to jointly hoist the pipe truss. When the two machines lift the hook at the same time to move the pipe truss about 1.5m off the ground, check whether the position of the wire rope, the snap ring and the binding point is accurate. In order to prevent the truss from swinging left and right during the lift-off and easy installation, both ends of the truss are tied with control cables of no less than 25m, and each control rope is equipped with at least 2 people. After the pipe truss reaches the top of the column, the brakes are used for alignment work. 4 people on each side take the ladder to the top of the column, enter the safety basket and fasten the safety belt on the beam between the columns. After the line is aligned, temporary fixation is performed, and verticality correction and final fixation are performed at the same time. After calibration, tighten the anchor bolts or electric welding for final fixation. When the electric welding is finally fixed, the welding should be applied from the same side at both ends to avoid the pipe truss tilting due to the shrinkage of the welding seam. After welding, the hook can be unloaded
(4)Temporary support and installation.
After the truss is hoisted in place, the supporting tie rod is immediately used to pull and fix the steel beam or the previous truss to form a stable system, and then the next truss is hoisted successively.

3 Control points of pipe truss hoisting
(1)Unified command and mutual cooperation.
The two-machine lift must be commanded by the two machines so that the two cooperate with each other and coordinate their actions. During the entire hoisting process, the hook pulley blocks of the two cranes should be kept vertical. Both ends of the lower chord of the pipe truss are tied with sliding ropes, so as to control the swing of the pipe truss during the hoisting process of the pipe truss and avoid collision with the boom of the crane and other surrounding facilities.
(2)Lift slowly.
The pipe truss should be lifted slowly. When the pipe truss is about to leave the ground, stop for half a minute and then continue to lift. When it is 500mm away from the ground, observe the pipe truss, crane, and spreader. Fix the steel wire rope to correct the verticality and lateral deflection of the pipe truss within the allowable deviation range of the specification, and then fix it firmly. After it is completely fixed according to the requirements of the drawing, loosen the hook to install the next steel truss.
At present, the domestic truss structure is developing towards a larger span and a larger height, which also puts forward higher requirements for the quality of truss construction. Therefore, it is necessary to put forward higher requirements for the corresponding quality control of truss construction.







 About Us
About Us 2023-01-13
2023-01-13



