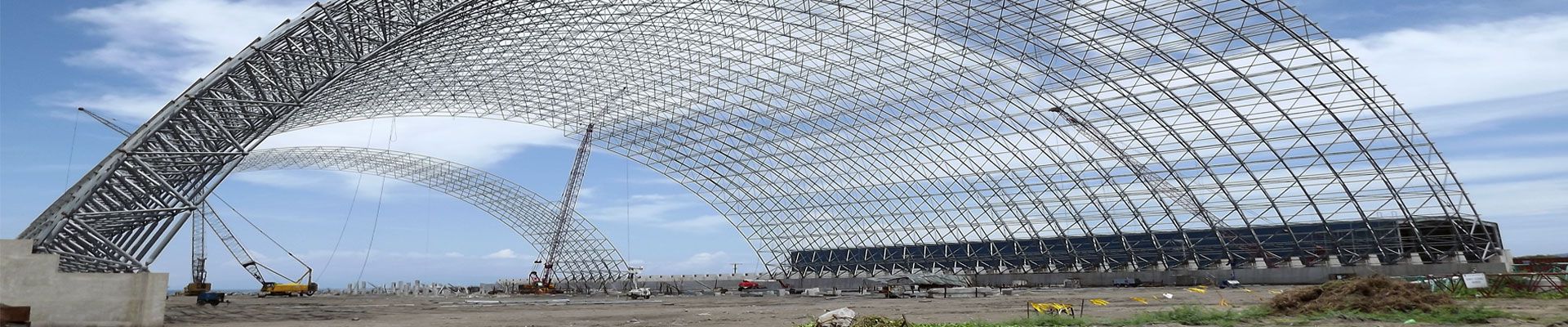
The roof system is a critical component of factory structures, and its safety directly affects the stability and overall safety of the building. The safety of the roof system not only impacts the normal operation of production lines but also directly concerns personnel safety. Most factory collapse incidents are closely related to issues with the roof system, making the inspection of roof system safety hazards crucial.
Based on years of experience in inspecting and assessing industrial buildings, the main safety hazards of factory roof systems include: severe dust accumulation on the roof, debris accumulation in gutters, storage of materials on the roof, addition of photovoltaic panels on the roof, rust and damage to roof panels, durability issues with concrete roof panels, connection issues at the ends of the roof truss chords and vertical rods, connection problems between truss supports and columns, deformations of truss members, un-welded intersections of horizontal supports, non-standard connections at truss joints, and missing tie rods for purlins.
Case Study:
Collapse Incident at Huanan Sports Center, Jiamusi City, Heilongjiang Province. On November 6, 2023, the roof of Yuecheng Sports Club collapsed. The building is a two-story frame structure with an area of approximately 2,000 square meters, resulting in three fatalities.
Collapse Cause Analysis:
1.Overloading:
During use, materials were stacked beyond the design load capacity, causing excessive structural load and leading to collapse.
2.Excessive Dust Load:Failure to promptly clear dust accumulation on the roof increased the load beyond the regulatory limits, raising the risk of collapse.
3.Unapproved Structural Modifications:
Unauthorized changes to the factory structure and usage by the owner or users, without professional assessment, increased the risk of collapse.
4.Structural Damage:
Various forms of damage, such as member rust, reduced cross-sectional strength, etc., resulted in insufficient load-bearing capacity and eventual collapse. Specific issues included deformations in truss members affecting load transfer, increased corrosion risk due to roof damage, and durability problems such as exposed and rusted reinforcement in concrete roof panels and concrete spalling.
Insufficient Stability of Steel Structures:
1.Design Defects:
The design phase failed to adequately consider structural stability requirements, resulting in the building’s inability to effectively distribute and withstand loads.
2.Material Issues:
The quality of construction materials did not meet standards, failing to satisfy the design’s material performance requirements, affecting overall structural stability and safety.
3.Non-standard Structural Layout:
During construction, deviations from design drawings and technical standards reduced structural stability. For example, missing purlins, supports, or inadequate reinforcement due to excessive space between columns and foundations.
Impact of Natural Disasters:
1.Strong Winds:
High winds are a direct cause of industrial building collapses. Under wind loads, structures may undergo irreversible deformation, leading to total collapse.
2.Heavy Rain or Snow:
Extreme weather conditions, such as heavy rain or snow, increase the load on the roof. Exceeding the structural load capacity leads to irreversible deformation and eventual collapse.
3.Geological and Topographical Factors:
Poor geological conditions or topography that increases wind speed at the site can also heighten the risk of collapse.
Inadequate Maintenance and Inspection:
1.Lack of Routine Maintenance:
Absence of regular inspections and maintenance of the factory structure allows minor issues to accumulate into major problems, ultimately leading to structural failure.
2.Delayed Damage Detection:
Failure to promptly identify and repair cracks, deformations, and other damage exacerbates structural issues.







 About Us
About Us 2024-10-11
2024-10-11


